What is Request (REQ)? Crypto Token for Businesses Explained
Request has made a significant impact to the crypto ecosystem, because it’s useful to many blockchain-based businesses, and not rarely, individual consumers.


Digital payments mold the foundation of our global and interconnected economy. Yet, we often take it for granted, and we rarely even think about the problems and inefficiencies associated with the way we pay businesses remotely.
In fact, saving this problem can save buyers and sellers a lot of money — for example, by removing the middleman, making payment gateways user-friendly, and processing transaction data automatically for accounting purposes.
Key takeaways:
- The Request Network enables two parties to transfer and/or transact cryptocurrencies securely.
- Businesses using the Request Network are able to verify their transaction histories reliably using the network.
- Request makes it easy for businesses, organisations, etc to keep track and record financial stats for easy auditing, calculating tax requirements for compliance, and much more.
What is Request (REQ) token?
The Request Network (shortened as simply Request) is a blockchain-based network that allows two parties to transact cryptocurrencies safely and conveniently.
The Request Network makes use of blockchain technology to enable two parties to transact crypto assets in a convenient and safe environment.
Now, unlike a more traditional method where the payer sends an amount of crypto to the payee, the Request network reverses the role. It makes it easy for the payee to create an invoice or bill to the payer via a smart contract, and have the payer accept the payment request.
This already anticipates the problem in cryptocurrency payment systems where the payer may potentially enter the wrong crypto address. If instead the payee has accidentally sent the payment request to the wrong address, the recipient of that request can simply ignore it.
Of course, Request also offers more solutions other than this small blunder that is easy to miss. Businesses that are connected to the Request Network can verify their transaction history from a single source of truth.
This potentially creates an error-free system in which the accounting management of all parties involved can rely on.
Also read: What is blockchain technology?
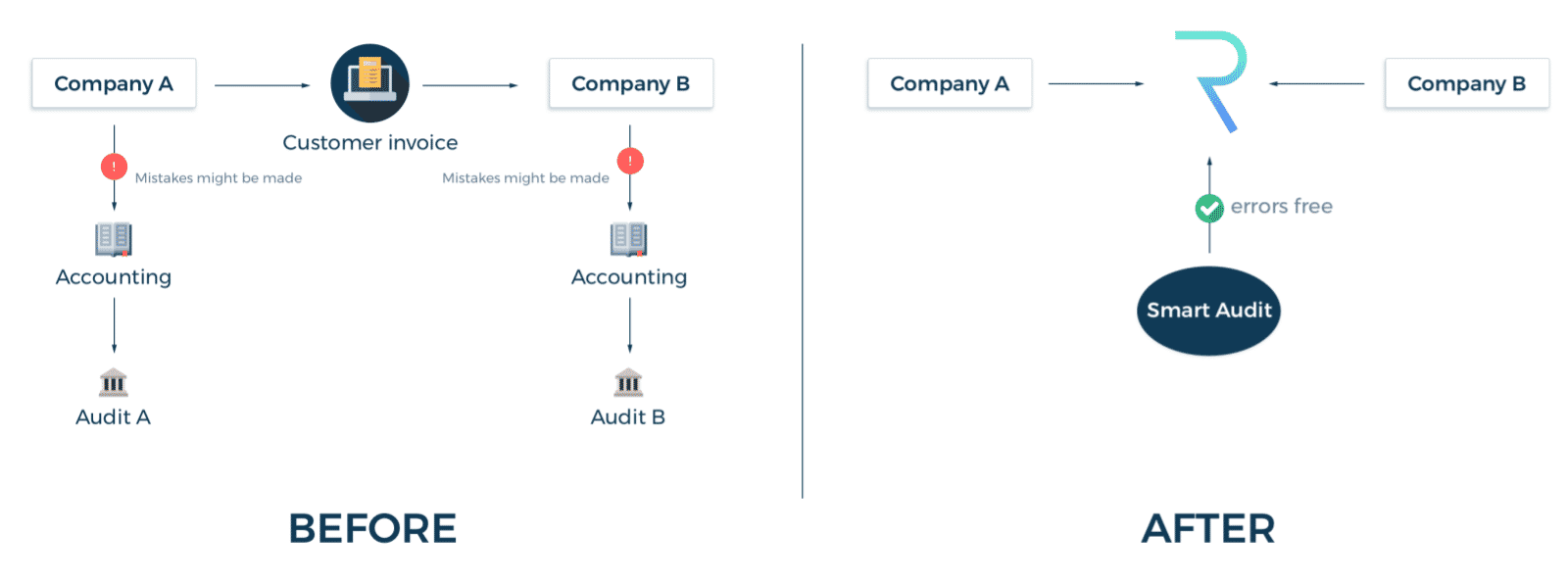
From tax purposes to simply keeping track of personal spendings, Request can help all manner of users to automatically audit and analyse their transaction history. This is because Request allows users to create and manage smart digital invoices.
When I say digital invoices, I don’t mean invoices which are sent to customers in PDF format. If that’s the case, then customers would have to copy the invoice data again into their own separate system. What Request does instead is to unify all accounting logic into the smart contract and smart invoices.
If you’re a business, and you send a payment request, both you and your customers (assuming both use Request) don’t have to input any more data into a separate system. Everything is built-in for easy accounting.
What is the REQ token?
Request is actually a decentralised application, meaning that it is built on top of existing blockchains. Request started running on Ethereum, making most REQ tokens in circulation an ERC-20 token.
It’s important to note all REQ tokens will hold the same value, regardless of its blockchain host.
The code behind Request is flexible enough to allow REQ tokens to exist on other blockchains (though not as an ERC-20 token). Part of the goal of Request is to become blockchain agnostic.
This means businesses can use Request even if they primarily use other blockchains, given that Request is ready to be built on that blockchain.
The REQ token is technically not the means of payment, although any two or more parties can transact in REQ tokens as it holds value. However, it was designed to facilitate transactions.
Fees are paid in REQ, which gets swapped by the network to whichever cryptocurrency is needed to update the specific blockchain.
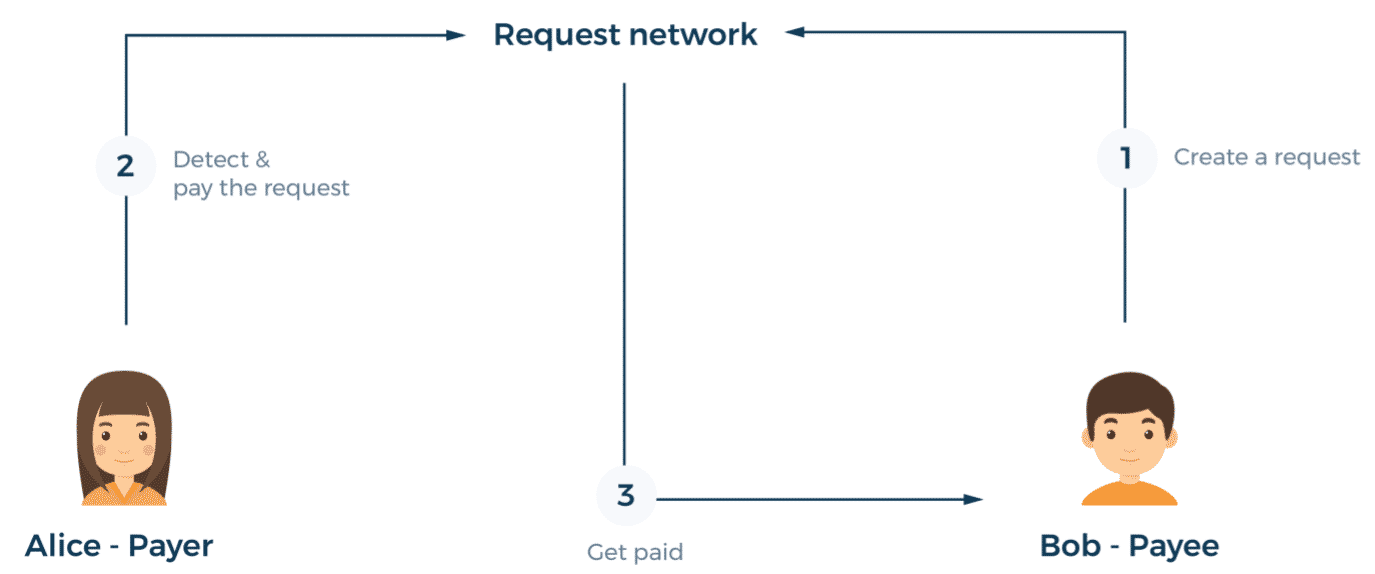
So, if someone were to request payment in Ether on the Ethereum blockchain, the payee should have enough REQ in their balance. The payer can easily pay the total sum of the amount due (which already includes the transaction fee).
The REQ token signals a series of smart contracts which sends Ether to the payee, while swapping REQ tokens for Ether to pay for gas. Swapped REQ tokens are sent to a burning address where it is locked up forever.
The payer doesn’t necessarily have to pay the full amount of gas for an Ethereum transaction. Request is smart enough to reduce transaction costs, through some intricate combinations of algorithms which involve liquidity pools. But this is beyond the scope for an introductory guide on Request.
Tokenomics of REQ token
Here’s a brief tokenomics data on the REQ token. The company behind Request uses a common business model where they would create and issue the entire supply of the REQ token, which is capped at 1 billion REQ tokens.
At the time of writing, 22.4% of the supply is in the hands of the Request Foundation, which is responsible for maintaining the code in a decentralised manner by means of decentralised voting and governance. 21.4% of tokens are on various exchanges, which are being used by active traders, while the remaining 56.2% are in private wallets.
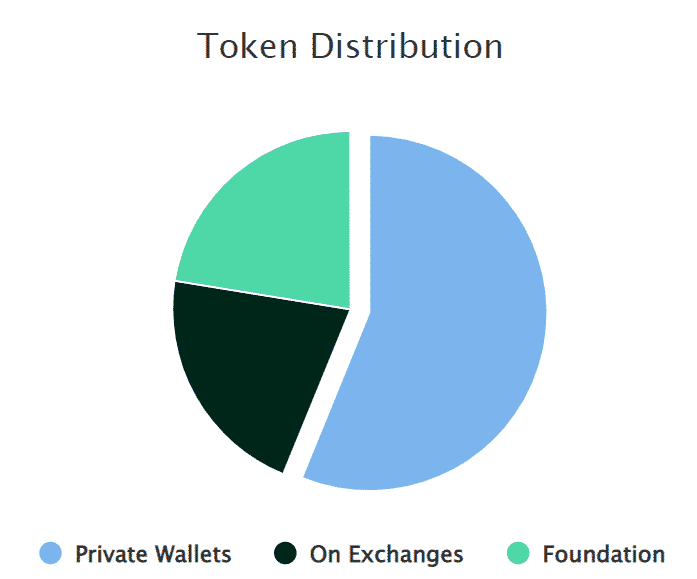
This shows that REQ is some of the most well-distributed tokens. It’s believed that if too many of the tokens or cryptocurrencies are in possession of a “foundation” — even if the decision-making is decentralised — there is a risk of a great liquidation through a backdoor access to these funds.
Therefore, there is a considerably smaller risk for “token dumping” should the price of REQ fall below its value.
How useful is Request (REQ) to the crypto ecosystem?
Unknown to many, Request has made a significant impact to the crypto ecosystem, because it is useful to many blockchain-based businesses, and not rarely, individual consumers.
At the end of the day, the crypto ecosystem is composed of businesses who want to profit from crypto trading, mining, shared computation, and decentralised data storage.
There are real business leaders, CEOs, community heads, and chief of finance behind every brilliant project in the ecosystem, such as Aave, Maker, Fantom, and many more.
These foundations, organisations, or firms make use of Request to organise their finances where checks and balances are littered with ticker codes of a myriad of cryptocurrencies.
Fortunately, with the use of smart digital invoices, Request can summarise financial stats for easy auditing, and calculate tax requirements to ensure compliance to financial authorities.
From large firms to small businesses with a simple web interface, Request can be integrated easily, for example, with a WooCommerce web plug-in called Wooreq, or with a more business-ready software called Request Finance.
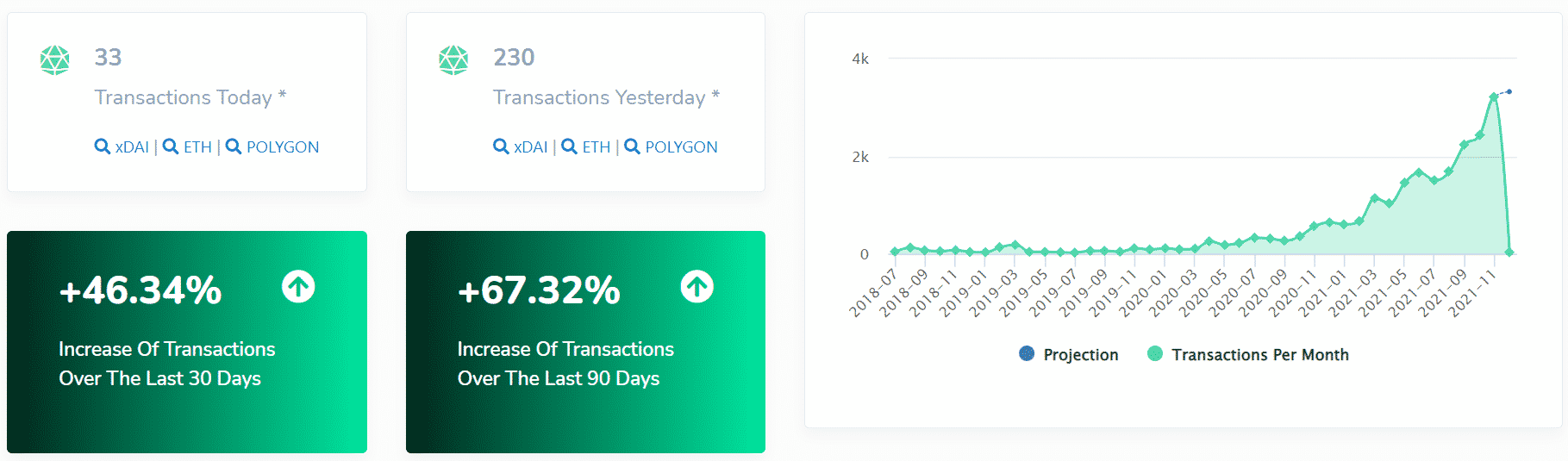
There is also a way to verify that Request is useful. If you go to the Request Network stats, you can see all the relevant figures that reflect the activity of the network. You can find things like:
- The number of REQ wallets in existence
- Transactions by day, week, month, and year
- Number of REQ tokens burned since project launch
- Current REQ supply
- The Foundation’s reserve REQ supply
- Token distribution (which we talked about in Tokenomics)
In fact, Request has grown in popularity recently, and there are places where you can “stake” your REQ tokens to earn passive income, for example, on Bancor DEX.
The Request Network also relies heavily on Kyber Network for its swap protocol in order to pay for blockchain fees. This makes both the KNC and REQ tokens valuable when more users pool into the network and make use of their service.
Are you bullish on Request (REQ)?
Request got even more attention in November 2021 when the NFT game giant Sandbox partnered up with Request to handle payment. The price of one REQ token quadrupled in a single day.
It’s really not important to pay attention to how far the price can go up in such a short span of time. The fact that blockchain game developers are considering to use Request in their system means that Request is not only useful in DeFi, but also in other realms across the crypto ecosystem.
If you believe that Request (REQ) has a massive potential, go get some REQ tokens today.
How to Buy Request (REQ) in New Zealand
With that being said, what are your own thoughts on Request (REQ)?
As cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology continue to mature and enter mainstream usage, the utility of the Request Network will become invaluable for businesses and/or individual who wish to scale their operations.
If you believe in the underlying technology of REQ, perhaps it is one asset that is worth diversifying your portfolio into. You can do so easily with Easy Crypto New Zealand, where you can buy REQ with NZD seamlessly.
Latest rates for REQ to NZD: Use our crypto converter tool to check the rates for REQ/NZD.
Buy REQ: Add REQ to your crypto portfolio.
Request (REQ) is just one of over 160+ altcoins that we offer at Easy Crypto New Zealand. Our collection consists of NFT tokens, Metaverse, DeFi, stablecoins and many more.
Start here: Read our quick guide on how to buy crypto in New Zealand.
Or check out our YouTube channel for a video guide!
Stay tuned for more crypto coin guides! In the meantime, explore our library of crypto coin fundamentals on our learning hub at Easy Crypto.
Share to
Stay curious and informed
Your info will be handled according to our Privacy Policy.
Make sure to follow our Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and YouTube channel to stay up-to-date with Easy Crypto!
Also, don’t forget to subscribe to our monthly newsletter to have the latest crypto insights, news, and updates delivered to our inbox.
Disclaimer: Information is current as at the date of publication. This is general information only and is not intended to be advice. Crypto is volatile, carries risk and the value can go up and down. Past performance is not an indicator of future returns. Please do your own research.
Last updated December 13, 2022





